The world we perceive is just a sliver of the electromagnetic spectrum. Beyond the visible light we see, lies a fascinating realm of invisible radiation, including ultraviolet (UV) light. While invisible to the naked eye, UV light has a multitude of applications, and UV torches have become essential tools in various fields. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of UV torches, exploring their properties, applications, safety considerations, and how to choose the right torch for your needs.
Understanding Ultraviolet (UV) Light
UV light is a type of electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than visible light but longer than X-rays. It exists on a spectrum further subdivided into three main categories:
- UVA (315 nm – 400 nm): This type of UV light has the longest wavelength and is the least energetic. It penetrates deep into the skin and is a significant contributor to sun tanning and sunburn.
- UVB (280 nm – 315 nm): This medium-wavelength UV light is responsible for most of the skin’s tanning and burning effects. It is also used in some medical applications like psoriasis treatment.
- UVC (100 nm – 280 nm): The shortest and most energetic form of UV light, UVC is germicidal, meaning it can kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. However, due to its harmful effects on human skin and eyes, UVC light is typically only used in controlled environments.
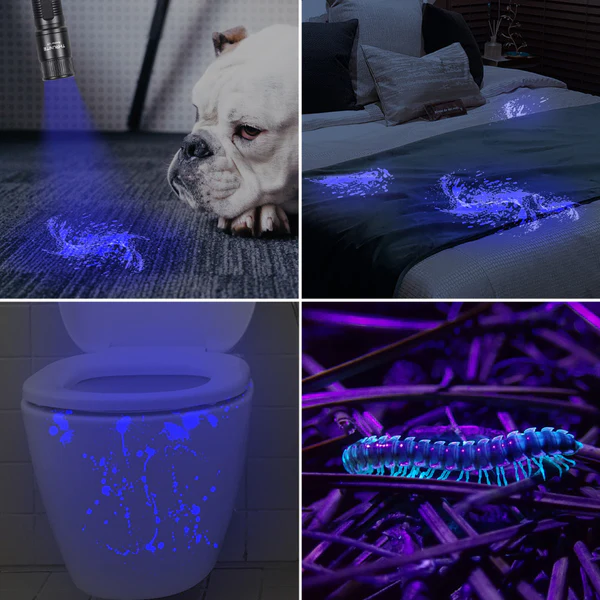

Exploring the Applications of UV Torches
- Scorpion Detection: Scorpions often glow a fluorescent blue under UV light, making them easier to spot at night. This is particularly useful for pest control professionals and homeowners in scorpion-prone areas. [Link to relevant UV torches]
- Mineral Identification: Certain minerals fluoresce under UV light, revealing their presence and aiding geologists and rockhounds in mineral exploration. [Link to relevant UV torches]
- Art and Antique Verification: UV light can help identify forgeries or restorations in paintings and antiques. Restorers also use UV light to distinguish between different varnishes and materials.
- Leak Detection: UV light can be used to detect leaks in air conditioning systems, plumbing fixtures, and even car engines. Certain dyes that fluoresce under UV light are used to pinpoint the location of the leak.
- Crime Scene Investigation: Bodily fluids, fingerprints, and other forensic evidence can sometimes be revealed or enhanced using UV light, aiding law enforcement investigations.
- Currency Verification: Some security features on banknotes fluoresce under UV light, helping to identify counterfeit bills.
- Air Quality Inspection: Airborne contaminants like mold spores can sometimes fluoresce under UV light, aiding in air quality inspections.
- Pest Control: UV light can be used to attract insects for easier detection and control.
- Industrial Applications: UV light is used in various industrial processes, such as curing adhesives and inks.
- Medical Applications (Limited): While UVC germicidal light is typically used in controlled environments, some specialized UV torches are used for localized disinfection in medical settings. Always consult a medical professional before using UV light for any medical purpose.
Safety Considerations When Using UV Torches
While UV torches offer a wide range of benefits, it’s crucial to prioritize safety when using them. Here are some key points to remember:
- Avoid Direct Eye Exposure: UV light can damage the eyes, so never look directly into the beam of a UV torch. Even brief exposure can cause corneal sunburn, a painful condition that can temporarily impair vision.
- Skin Protection: Prolonged exposure to UV light can cause skin damage similar to sunburn. Wear protective clothing and gloves when using a UV torch for extended periods.
- Safe Storage: Keep UV torches out of the reach of children and pets.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safe operation and recommended applications for your specific UV torch.
Choosing the Right UV Torch for Your Needs
With a variety of UV torches available, selecting the right one depends on your intended use. Here are some factors to consider:
- UV Wavelength: The most crucial factor is the UV wavelength emitted by the torch. For most applications, a torch with a UVA wavelength (365 nm – 400 nm) is sufficient. Scorpion detection and some mineral identification may require a torch with a slightly higher UVA range. Germicidal applications require UVC light (around 254 nm), but these torches should only be used with proper safety precautions and by trained professionals.
- Light Output Power: The light output power determines the intensity of the UV beam. Higher
- Light Output Power: The light output power determines the intensity of the UV beam. Higher power LEDs will provide a stronger and more effective UV light.
- Beam Focus: Some UV torches have adjustable focus, allowing you to switch between a focused beam for close-up inspection and a wider beam for larger areas.
- Power Source: Most UV torches use batteries, such as AA, AAA, or 18650 batteries. Consider battery life and ease of replacement.
- Durability: Look for torches with durable construction, such as aluminum or stainless steel housings, to withstand wear and tear.
- Ergonomics: Choose a torch that is comfortable to hold and easy to use.
- Safety Features: Some UV torches may include safety features such as an automatic shut-off timer or a protective lens.
Explore Our Selection of UV Torches
Safety Precautions
- Never look directly at the UV light beam.
- Wear appropriate eye protection when using UV light.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to UV light.
- Use UV light responsibly and in accordance with all relevant safety guidelines.
Conclusion
UV torches are versatile tools with a wide range of applications. By understanding their properties and choosing the right torch for your needs, you can safely and effectively utilise this technology in various fields, from pest control to scientific research.